Femoral Acetabular Impingement (FAI)
Femoral acetabular impingement is a condition that occurs when there is the development
of bone spurs on either the acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis or the femoral head or even
on both of those locations. Because of the friction that occurs between them, the bone
overgrowths start to restrict the range of motion in the joint. Because of this, the joint
cannot move in a fluid manner. Not only that, but it also has the potential to trigger an
increase in inflammation in the tissues that are nearby.
Anatomy
The hip joint is the largest ball and socket joint in the body. It is a joint between the pelvis
bone and thigh bone (femur). There is a round socket (acetabulum) in the pelvic bone, and
a large ball-like head of femur bone glides in it. The acetabulum is surrounded by a fibrous
tissue called the labrum.

impingement) or of the femoral head (cam impingement), or of both the bones (combined
impingement).

Signs and Symptoms
Bone overgrowth will naturally result in friction between the two moving bones, causing
pain, inflammation, and a limited range of motion. Thus, there would be joint stiffness and
limping. The character of pain may differ among individuals. Generally, standing still may
not cause significant pain, but squatting or twisting the leg may result in sharp pain. In
some, there may be just a dull pain.
Causes
It is a bone growth deformity, meaning that bone in an individual does not grow normally
during childhood, resulting in defects. As a result, some individuals may not have any
symptoms for long and may develop late when damage to the joint cartilage or other
structures starts.
Risk factors
It is a developmental disorder, and little is known about the risk factors.
Diagnosis
Physical examination
Osteoarthritis is the leading cause of hip joint pain. However, it affects older adults. Unlike
osteoarthritis, FIA is first diagnosed in physically active and relatively young adults.
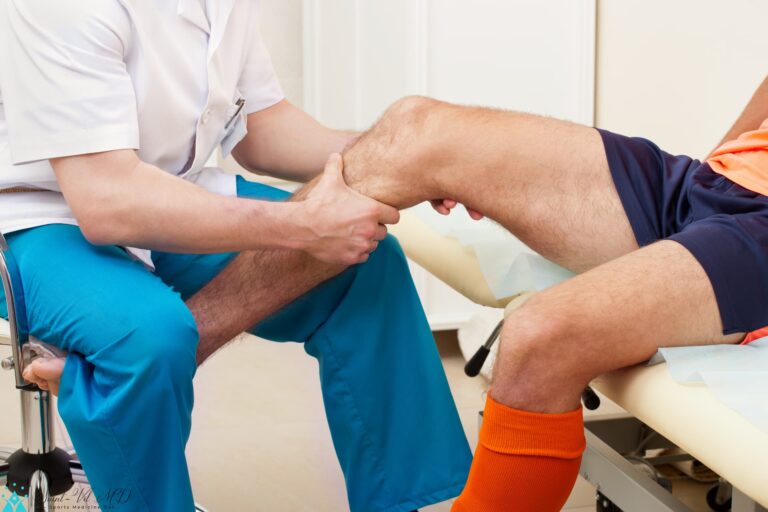
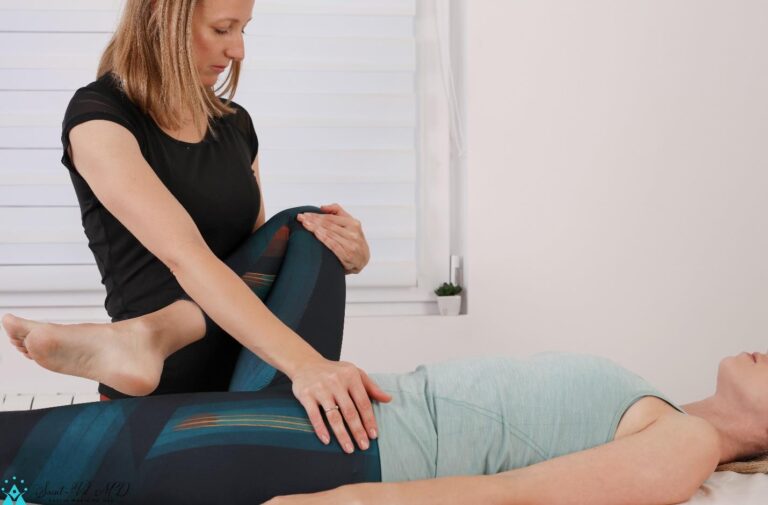
Additionally, doctors may carry out an impingement test in which the patient lies on the
back on the examination table. Then, the doctor tries to bring the knee upward towards
the patient’s chest, which would cause pain resulting in the positive impingement test.
Imaging
Since there is a bone overgrowth in the condition, an x-ray may be sufficient to confirm
the diagnosis and exclude arthritis. However, MRI may show damage to the surrounding
tissues more clearly.
Treatment
Home remedies
Since the bone overgrowth cannot be reversed, one may benefit from avoiding certain
motions that cause pain, which may help prevent the progression of the condition.
Non-surgical treatment
Among non-surgical treatments, doctors may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs. Additionally, physical therapy may help increase the range of joint motion and
reduce joint stress.
Surgical treatment
In severe cases, surgical correction might be the treatment of choice. Doctors may carry
out the surgical procedure with the help of arthroscopy and remove the bone overgrowth.
However, if the condition is severe, it may require a larger incision and open operation.
Prevention
It is a developmental disorder, and doctors know little about its cause. Thus, there is
nothing one can do to prevent the condition. However, once diagnosed, one can avoid certain types of motions that cause pain to slow down its progress or even arrest the growth
of bone spurs.